Overview
Let's prepare our dev environment and get to know the project we're building. In this lesson, we will:
- Verify our Apollo GraphOS account
- Set up our code environment
- Install and authenticate Rover
- Start a local project
What we're building
Let's meet our course project: Airlock.
Airlock is an intergalactic travel booking app, where we can find a cool place to stay in the wide open universe! You can find the demo project here: https://odyssey-airlock.netlify.app/
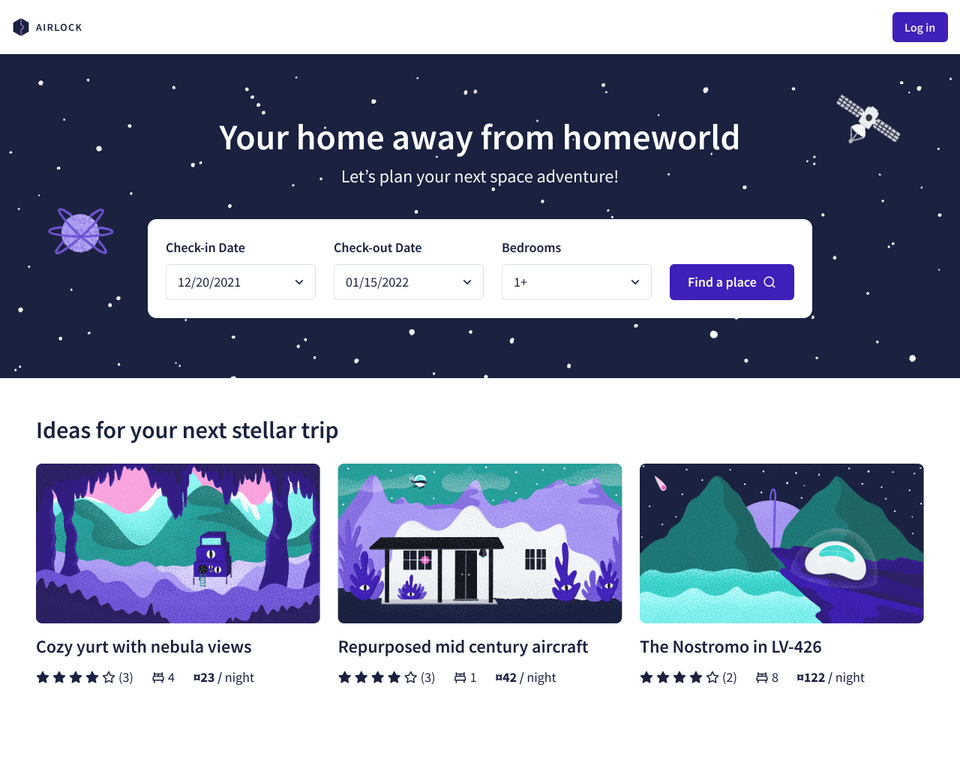
We'll be building the API for Airlock and we've got big plans, but right now, we'll start small.
We have a simple REST API with a few endpoints that let us explore the listings for our travels, giving us detailed information about places we could stay at, their amenities, how many beds and the cost.
You can find the REST API here: https://airlock-listings.demo-api.apollo.dev/
We'll use a few pages of Airlock mockups to guide us; we'll determine what pieces of data from which endpoints of the REST API we'd need to orchestrate.
We'll need a few things to get started. Follow the instructions below to set up the project!
1) Verify your Apollo GraphOS account
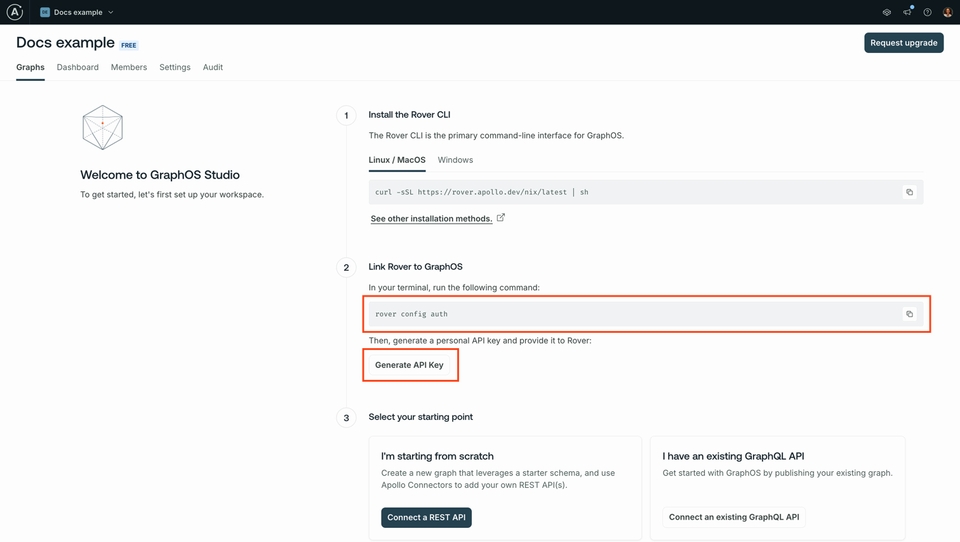
2) Install and authenticate Rover
You need at least Rover version v0.33.0 to complete this course.
3) Start a local project
4) Set up your code environment
5) Updating the schema with listings
Key takeaways
- To get started with Apollo Connectors, you need an Apollo account.
- To start up a local router for our API, we'll need to provide Rover with our graph credentials.
Up next
Rover will show a successful composition message, but we won't be able to query anything just yet. We're all set up, so let's dive into how we use Connectors in the schema.
Share your questions and comments about this lesson
Your feedback helps us improve! If you're stuck or confused, let us know and we'll help you out. All comments are public and must follow the Apollo Code of Conduct. Note that comments that have been resolved or addressed may be removed.
You'll need a GitHub account to post below. Don't have one? Post in our Odyssey forum instead.